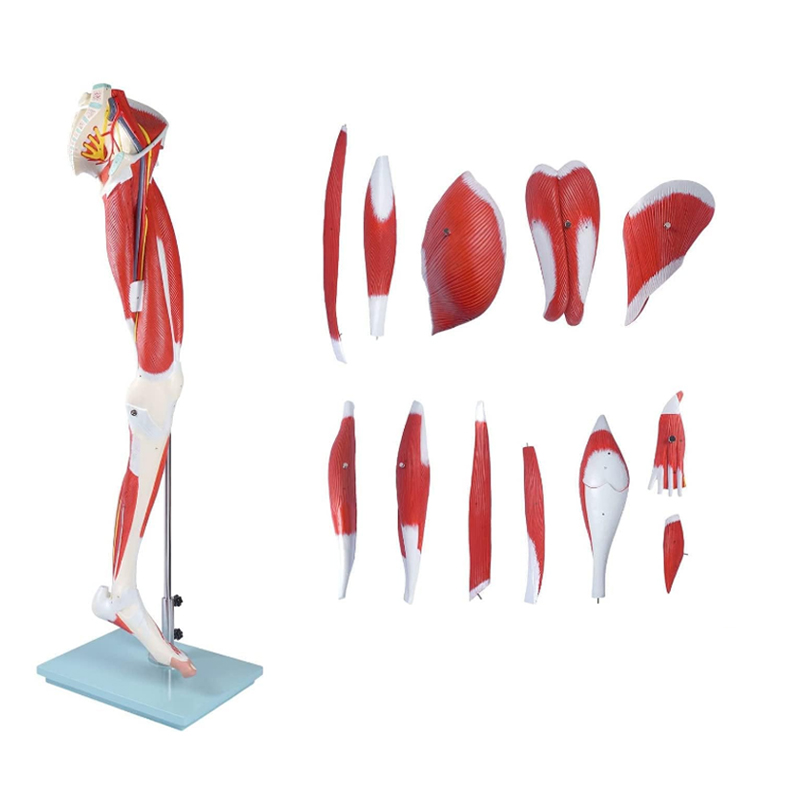
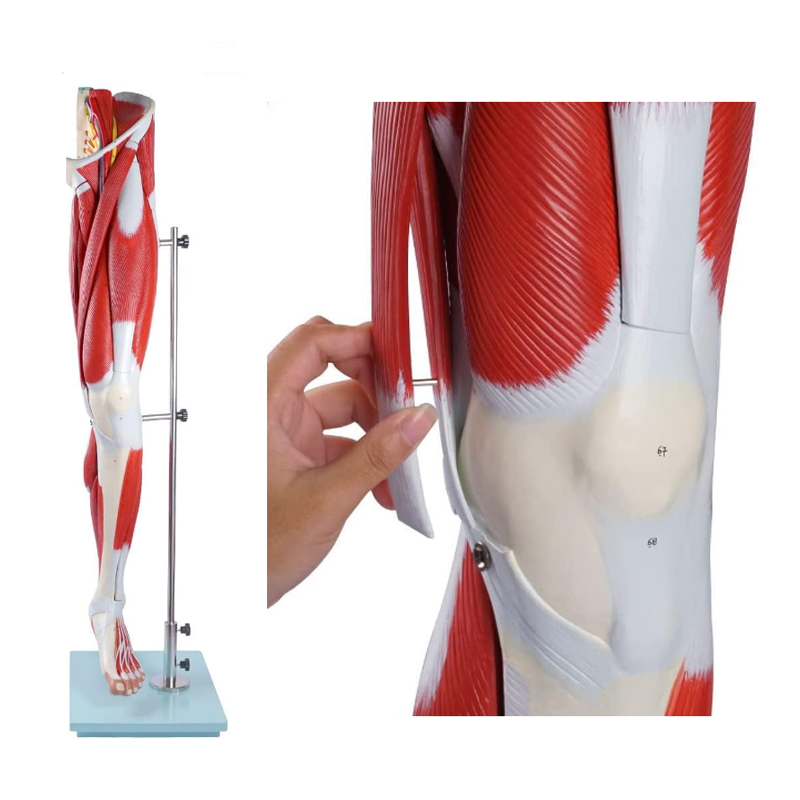
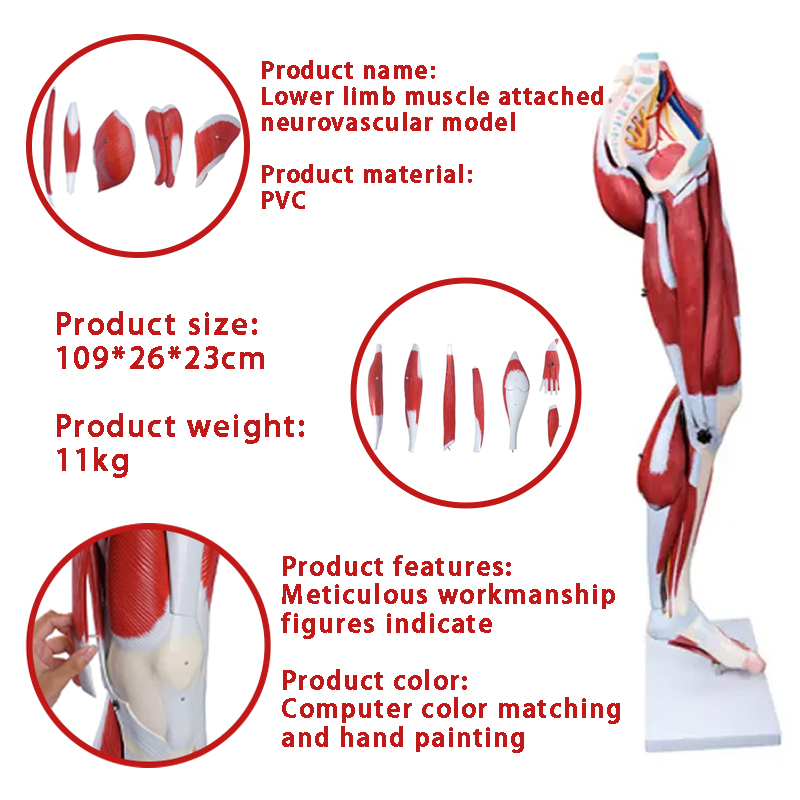
I. Precise Reproduction, Decoding the Lower Limb Muscular System
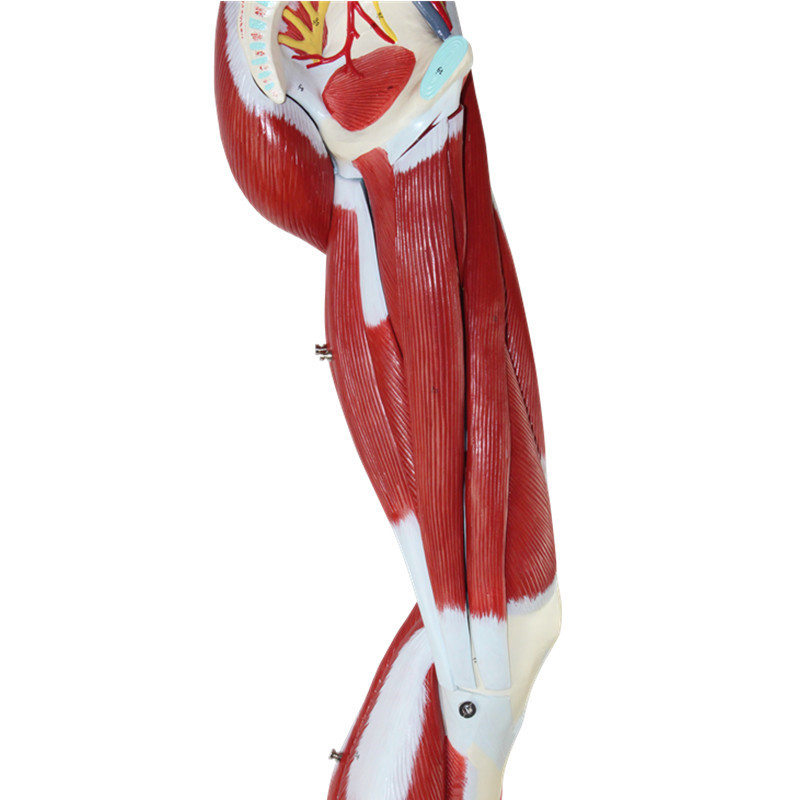
This model precisely replicates the distribution of muscles, nerves, and blood vessels in the human lower limbs at a 1:1 scale. From the contour of the quadriceps femoris in the thigh to the texture of the gastrocnemius muscle in the calf, and to the complex network of nerves and blood vessels in the popliteal fossa, all have been reviewed by professional medical teams. The details are clear and realistic, perfectly presenting the anatomical structure of the lower limb muscles, providing intuitive references for teaching demonstrations and clinical analyses.
II. Multi-Functional Applications, Meeting Multiple Domain Needs
Medical Education: Medical colleges can use this model for classroom teaching. By touching and observing the model, students can quickly master the knowledge of lower limb muscle anatomy and improve teaching efficiency;
Sports Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation institutions and fitness coaches can use the model to explain the principles of sports injuries (such as muscle strain and nerve compression) to patients and trainees, and formulate more scientific rehabilitation training and exercise plans;
Research Exploration: It provides physical references for lower limb muscle research and biomechanics analysis, assisting researchers in conducting in-depth projects.
III. High-Quality Materials, Balancing Durability and Safety
The model is made of environmentally friendly and durable polymer materials. It is shock-resistant and wear-resistant, and can be preserved for a long time. The surface coating is non-toxic and harmless, with a delicate touch, simulating the texture of human muscles. This ensures the safety of teaching use and prolongs the product’s lifespan, offering a much higher cost performance compared to similar products.
IV. In-depth Analysis of Product Advantages, Creating Core Competitiveness in Teaching and Research
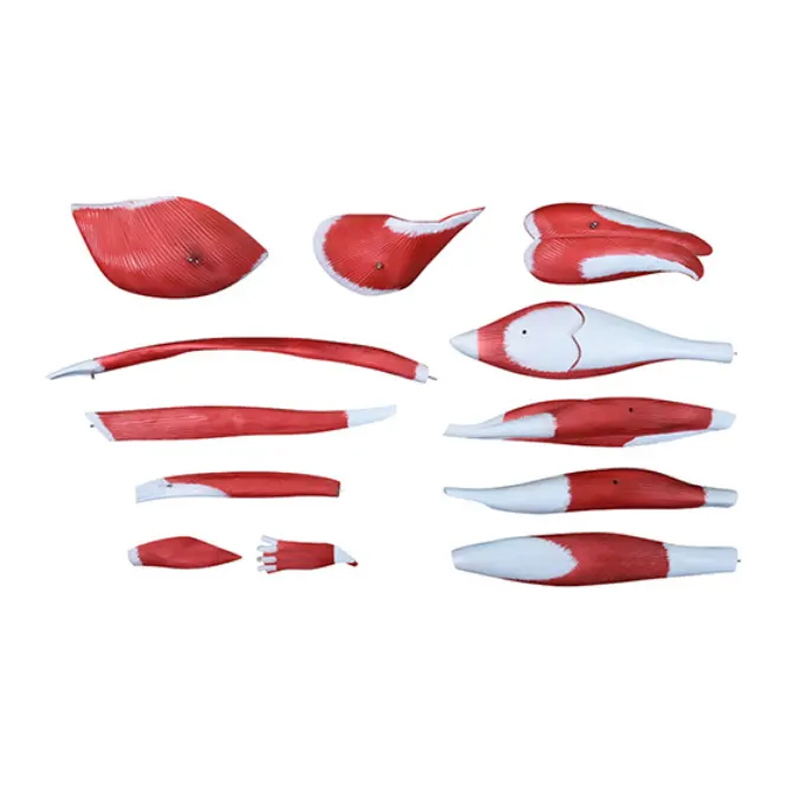
(1) Modular Splitting, Deep Exploration of Details
Different from traditional one-piece molded models, this lower limb muscle anatomy model supports modular splitting. For example, the quadriceps femoris group on the front of the thigh can be removed separately, clearly showing the muscle attachment points and the connection with the femur; the nerve and blood vessel bundles in the popliteal fossa can be split to demonstrate the branches of the sciatic nerve, the accompanying structure of the popliteal artery and the muscle. This design extends teaching from “overall observation” to “local anatomy”, meeting the needs of in-depth teaching research. Whether explaining muscle layers, nerve paths, or vascular anastomosis, it can precisely present.
(2) Dynamic Indicators, Reconstructing Physiological Interaction
The model innovatively incorporates the “Dynamic Physiological Interaction Indicators”. In the lower limb muscle part, special techniques are used to mark the pulling direction during muscle contraction and the joint linkage trajectory (such as the effect of gastrocnemius muscle contraction on ankle plantar flexion). In sports rehabilitation teaching, coaches can directly demonstrate the “muscle force – joint movement” interaction relationship, helping trainees understand “why the tension of the hamstring muscle affects knee flexion and extension”, making abstract sports anatomy knowledge more concrete and perceptible, significantly improving the professionalism of teaching and rehabilitation guidance.
(3) Data Annotation, Adapting to Precise Teaching and Research
The surface of the model adopts “Data-Encoded Anatomical Annotation”. For key muscles, nerves, and blood vessels, in addition to name identification, physiological parameters (such as reference values of the femoral artery diameter, the depth of the easy compression point of the common peroneal nerve from the body surface) are also annotated. Medical researchers conducting lower limb projects can directly obtain basic data references from the model; when clinical doctors explain “Key Points of Lower Limb Trauma First Aid”, they can combine the annotated blood vessel positions and the easily damaged areas of nerves to more accurately teach the key points of hemostasis and pressure reduction, upgrading the teaching aid from “structural display” to “data support tool”.
Post time: Aug-05-2025